Updated: 2026-01-15
Most of us spend hours each week doing the same repetitive tasks: copying data from emails to spreadsheets, filing documents, routing messages to the right people. Google Workspace Studio, released in December 2025, lets you delegate these tasks to AI agents that work inside Gmail, Drive, Sheets, and the other Google apps you already use.
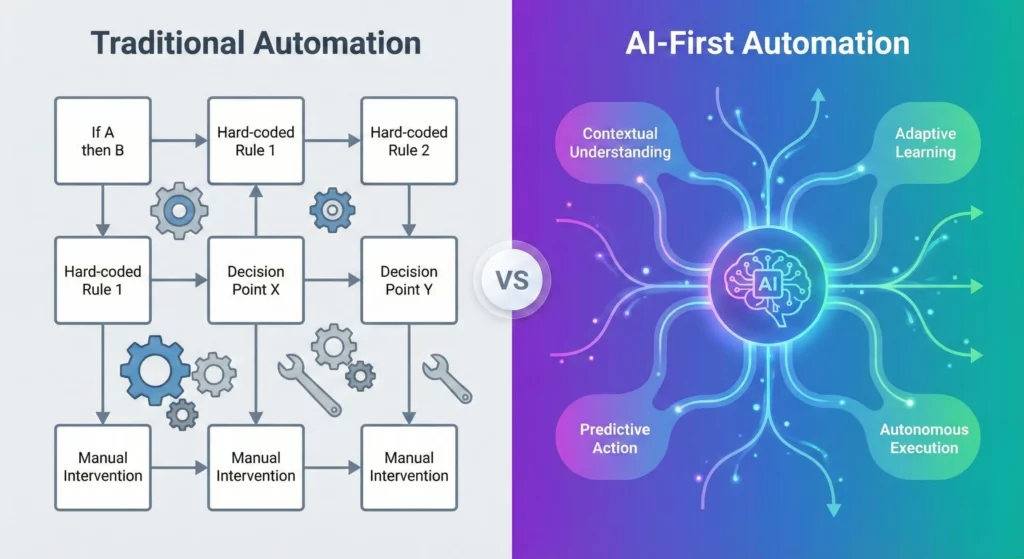
For nearly two decades, productivity software has meant clicking buttons, typing text, and manually moving information between applications. Automation existed, but it required technical expertise and rigid “if this, then that” logic. Google Workspace Studio changes this by embedding the reasoning capabilities of Gemini directly into Gmail, Drive, Sheets, Calendar, and Chat. You’re no longer just using software to complete tasks, you’re designing intelligent agents to handle them for you.
This guide will show you exactly how to harness this new capability, whether you’re in HR, sales, operations, or any other role where efficiency matters.
📅 Important Rollout Update (January 2026)
Google Workspace Studio is currently rolling out in phases based on your organisation’s release track:
- Rapid Release domains: Extended rollout started December 3, 2025 (in progress)
- Scheduled Release domains: End user access begins February 2026 (specific date TBA)
Don’t have access yet? This is normal! Your organisation’s release track determines when you’ll receive access. Check with your administrator, or jump to the “Prerequisites and Access” section below to understand the rollout timeline and explore early access options.
Table of Contents
What is Google Workspace Studio?
Google Workspace Studio is a no-code platform at studio.workspace.google.com that lets you create “flows”; intelligent agents that connect your Google Workspace apps and make decisions on your behalf.
The critical difference from traditional automation tools is that Workspace Studio is AI-first. You define the intent (like “manage my inbox for urgent client issues”), and Gemini handles the execution logic. The system can distinguish between spam and a critical client complaint without you programming every possible scenario.
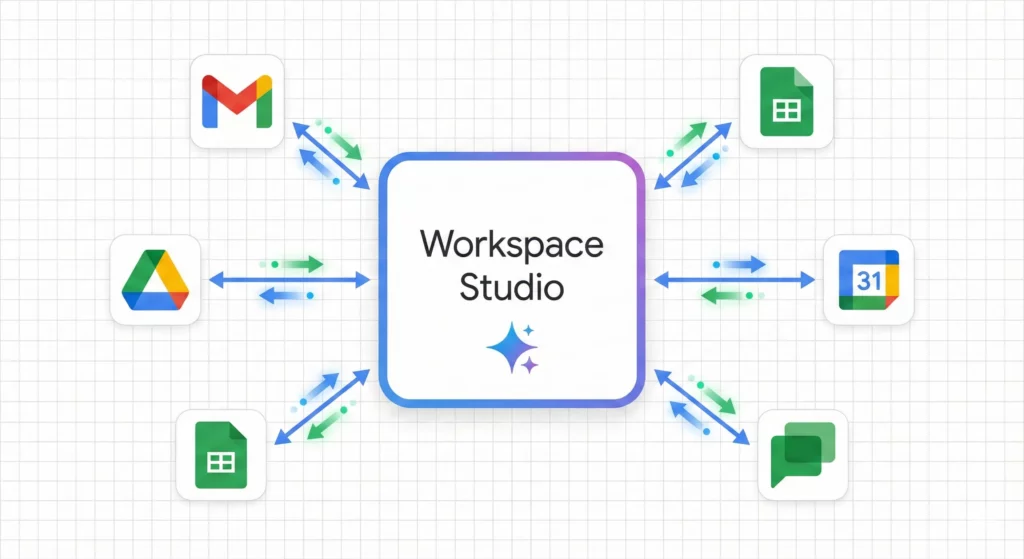
Think of Workspace Studio as connective tissue between previously siloed applications. A Google Form response no longer sits idle in a spreadsheet waiting for you to notice it. Instead, it becomes a living event that triggers emails, schedules meetings, and updates CRMs automatically.
Why Google Released This Now
By late 2025, employees were drowning in disparate AI tools. The constant switching between chatbot windows, email clients, and document editors created what’s known as “toggle tax” – the mental cost of context switching.

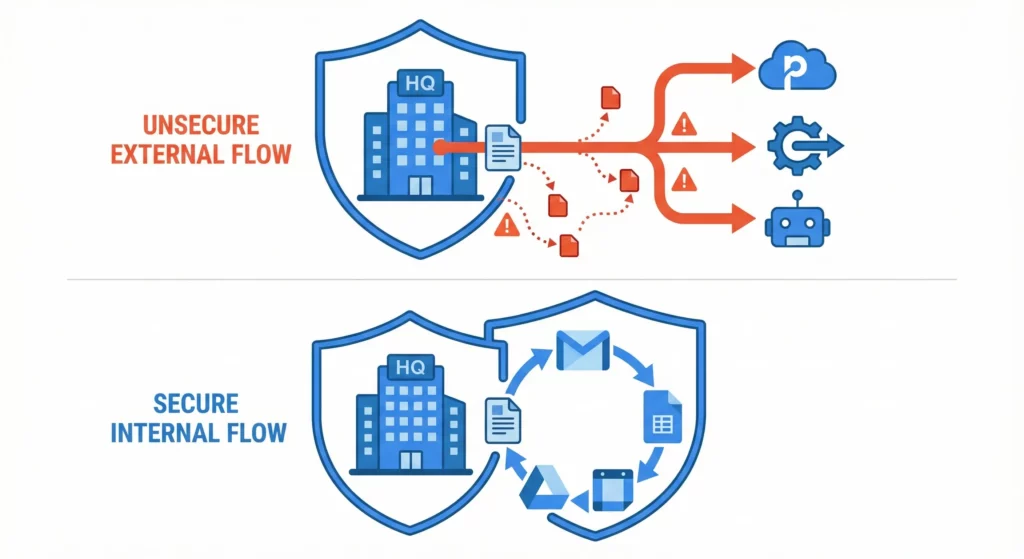
Google’s strategy with Workspace Studio is consolidation. By embedding intelligent automation inside your existing workspace, they address the two biggest barriers to enterprise AI adoption: context switching and data security.
There’s another factor at play. Employees were increasingly using unapproved tools like Zapier or personal ChatGPT accounts to automate their work. This “Shadow IT” posed serious risks to data governance. Workspace Studio brings automation activity back under organisational control, allowing administrators to monitor, audit, and manage how AI interacts with corporate data.
Understanding the Core Concepts
To use Workspace Studio effectively, you need to understand its specific architecture. The platform operates on four fundamental concepts: Starters, Steps, Variables, and the Intelligence Layer.

Starters: What Triggers Your Flows
Every flow begins with a single event called a Starter. This acts as an event listener waiting for a specific state change in your Google ecosystem. Currently, each flow can have only one starter; you can’t trigger the same flow from both an email and a chat message (you’d need two separate flows).
Starters fall into three categories:
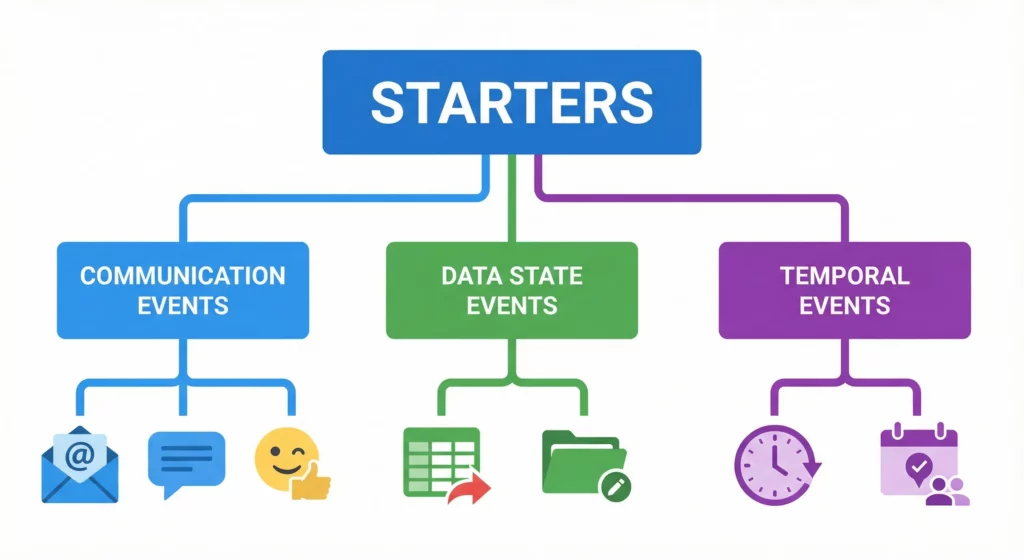
Communication Events
Communication Events trigger from human interaction. When I get an email is the most common, hooking into Gmail with pre-processing filters for sender, subject, and attachments. This filtering is crucial, without it, your flow fires on every marketing newsletter, quickly exhausting your daily limits.
When I get a chat message and When I'm mentioned enable “ChatOps,” transforming Google Chat into a command-line interface for your business. When an emoji reaction is added might seem trivial, but it unlocks powerful approval workflows. A manager can approve a document simply by reacting with a ✅, which the system interprets as permission to proceed.
Data State Events
Data State Events monitor changes to static data. When a sheet changes turns Google Sheets into a database with triggers, monitoring specific columns or rows for updates. This is particularly powerful for status tracking, when a “Status” column changes to “Done,” your flow can automatically notify stakeholders.
When a file is edited in Drive detects content changes (but not metadata changes like renaming or moving, which prevents infinite loops).
Temporal Events
Temporal Events trigger based on time. On a schedule works like a cron job for batch processing. Based on a meeting is unique – it carries event metadata (attendees, description, attachments) into your flow, enabling contextual preparation or follow-up actions.
Steps: The Execution Chain
Once a Starter fires, your flow executes a sequence of Steps. You’re currently limited to 20 steps, which enforces modular design over monolithic complexity.
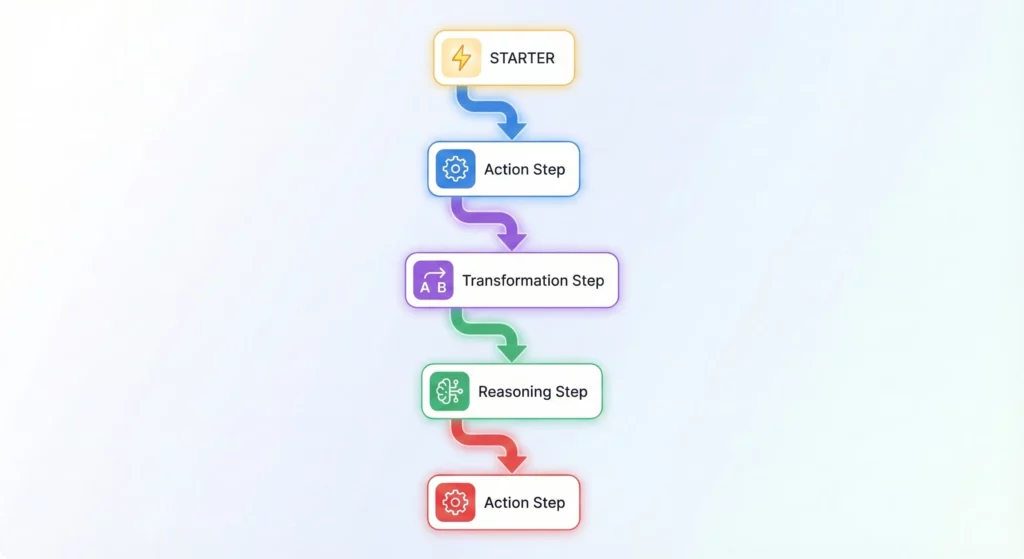
Action Steps are deterministic operations that interact with APIs: Send email, Create Drive Folder, Add row to Sheet, or Post Message to Chat.
Transformation Steps manipulate data in transit. The Extract step uses AI to parse unstructured text (like an invoice) into structured data (Invoice ID, Amount, Date).
Reasoning Steps differentiate Workspace Studio from traditional automation. The Decide step doesn’t just compare values, it evaluates semantic meaning. You can ask it to determine whether an email comes from a frustrated customer likely to churn. The Ask Gemini step allows for sophisticated prompt engineering within your flow, letting you guide exactly how the AI responds.
Variables: Your Data Pipeline
Data flows through your agent via Variables. When a Starter executes, it generates an object containing relevant metadata. A “New Email” starter generates Sender, Subject, Body, Date, and Attachments.
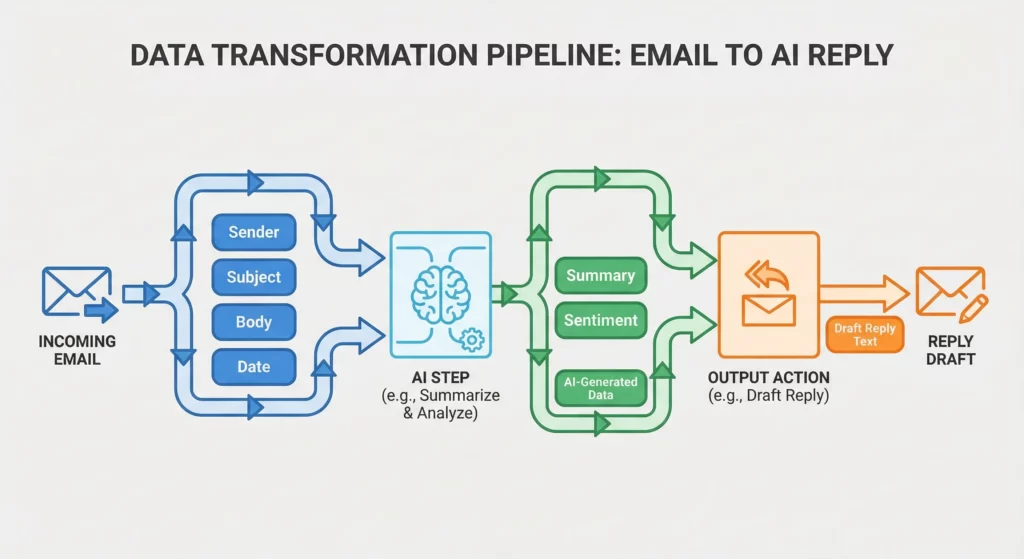
Subsequent steps can reference these variables. Your reply draft might use the Sender variable to address the recipient and a Summary variable from an AI summarisation step to generate content.
In the Workspace Studio interface, variables appear as chips you can insert into text fields. Understanding data types is critical here, a File variable (an object reference) can’t be placed into a Text field without causing errors or producing useless object ID strings.
The Intelligence Layer: Gemini
Google’s Gemini model underpins the entire system. Unlike traditional code that produces identical output for identical input, Gemini’s output can vary slightly in phrasing or tone. This probabilistic nature is a feature, allowing for creativity and adaptability in communication workflows.
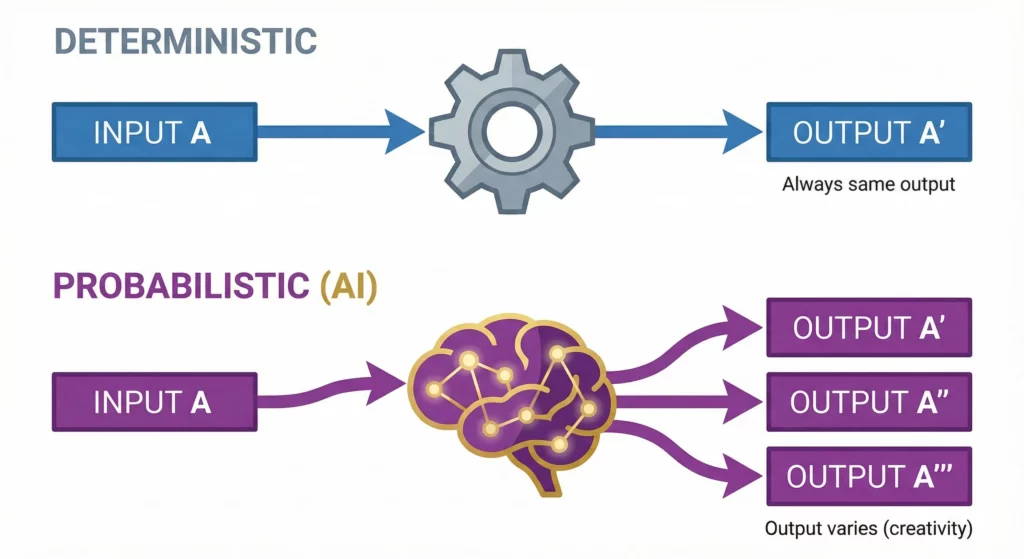
This requires a mindset shift. You need to design flows that are resilient to slight variations in AI output, often by using the Decide step to validate responses before taking action.
Getting Started with Workspace Studio
Prerequisites and Access

As of January 2026, Google Workspace Studio is rolling out to customers with the following editions:
- Google Workspace availability:
- Business Starter, Standard, and Plus
- Enterprise Standard and Plus
- Education Fundamentals, Standard, Plus, and the Teaching and Learning add-on
- Google AI availability:
- Google AI Pro for Education
- Google AI Ultra for Business
Understanding When You’ll Get Access
Google releases new features through two tracks. Your organisation’s administrator chooses which track to use, and this choice determines when new features like Workspace Studio become available:
Rapid Release – Access started December 3, 2025 (extended rollout in progress)
- Users are among the first to see new features
- Includes access to early GA (General Availability) features
- May experience different UI variations during testing
- Best for organisations that want to stay on the cutting edge
Scheduled Release – End user access begins February 2026 (specific date TBA)
- New features arrive at least one week after Rapid Release domains
- More time to prepare your organisation for changes
- More stable, predictable experience
- Recommended for production environments
How to Check Your Organisation’s Release Track:
Only administrators can see and change the release track setting:
- Sign in to the Google Admin console at admin.google.com
- Look for the “Release preferences” section
- Click “New features” to see your current track
If you’re not an administrator, simply ask your IT team: “Is our organisation on Rapid Release or Scheduled Release?”
How Administrators Can Switch to Rapid Release:
If your organisation is on Scheduled Release and you want earlier access to Workspace Studio and other new features, administrators can change the release track:
- Sign in to the Google Admin console at
admin.google.com. - Go to Menu and then
Account>Account settings>Preferences. - In the
Release preferencessection, clickNew features. - Select
Rapid release. - Click
Save.
Changes typically happen quickly but can take up to 24 hours.
Important Warning: If you switch from Rapid Release back to Scheduled Release in the future, your users might lose access to features currently only available on the Rapid Release track.
Administrative Setup
Before you can create your first flow, your Google Workspace Administrator and you must ensure several requirements are met:
Workspace Studio is a core service and will be on or off by default based on your organization’s release track setting.
- To Turn On Workspace Studio:
- Navigate to
Admin Console>Apps>Google Workspace>Workspace Studio. - Click
Service status. - To turn a service on for everyone in your organisation, click
On for everyoneand then clickSave. - Alternatively, enable it for specific organizational units or groups.
- Navigate to
- Enable Gemini Access:
- To use any AI-powered steps, such as “Ask Gemini” or “Recap,” your admin must explicitly enable Gemini on your account.
- Marketplace & Integration Setup:
- If you intend to use third-party connectors (like Salesforce or Jira), your admin may need to allow these integrations in the
Google Workspace Marketplaceor install a required helper application for specific services.
- If you intend to use third-party connectors (like Salesforce or Jira), your admin may need to allow these integrations in the
- Mandatory Gmail Settings:
- Even if the admin has enabled everything, your flows will fail to start if you have disabled smart features. You must go to your
Gmail Settings>Generaland ensure bothSmart featuresandGoogle Workspace smart featuresare toggledON.
- Even if the admin has enabled everything, your flows will fail to start if you have disabled smart features. You must go to your
- Platform Restriction:
- You must use a computer with a supported web browser to create or edit flows; Workspace Studio is currently not available on mobile devices for the creation process,
Don’t have access yet? Try the Gemini Alpha Program
If your organisation is on Scheduled Release and you don’t want to wait until February 2026, you can request that your administrator enable the Gemini Alpha program.
Important: The Alpha program gives access to ALL experimental Gemini features, not just Workspace Studio. This means you’ll see other pre-release features that are still in development.
How Your Administrator Can Enable Alpha Access::
As of April 22, 2025, all Google Workspace customers can access Gemini alpha features without needing a specific add-on.
- Sign in to the Google Admin console with an administrator account.
- Navigate to
Menu>Generative AI>Gemini for Workspace(Note: This requiresGemini Settingsadmin privileges). - Click on the
Alpha Gemini featurespanel. - On the left, choose to enable access for specific
Users,Groups, orOrganisational units. - Click
Onand follow the prompts to confirm.
What to Know About Alpha Access:
- All-or-Nothing:
- You cannot pick and choose which alpha features to enable, it’s all of them or none.
- Data Security:
- Alpha features follow the same data protection standards as core Google Workspace services. Your data is not used to train Google’s general AI models.
- Feature Availability:
- Some advanced steps (third-party connectors, webhooks, etc) may be in “Limited Preview” or temporarily unavailable as Google scales infrastructure.
- Not Required for Rapid Release:
- If your organization is already on Rapid Release, you don’t need Alpha access—you’re already in the rollout queue.
The Workspace Studio Interface
Access Workspace Studio at https://studio.workspace.google.com. The interface is divided into four primary workspaces:
The Discover Page is your entry point. It features a “Describe to Design” input where you can type natural language requests like “Create an agent that saves invoices to Drive.” It also houses pre-built templates categorised by role (Sales, HR, Admin).
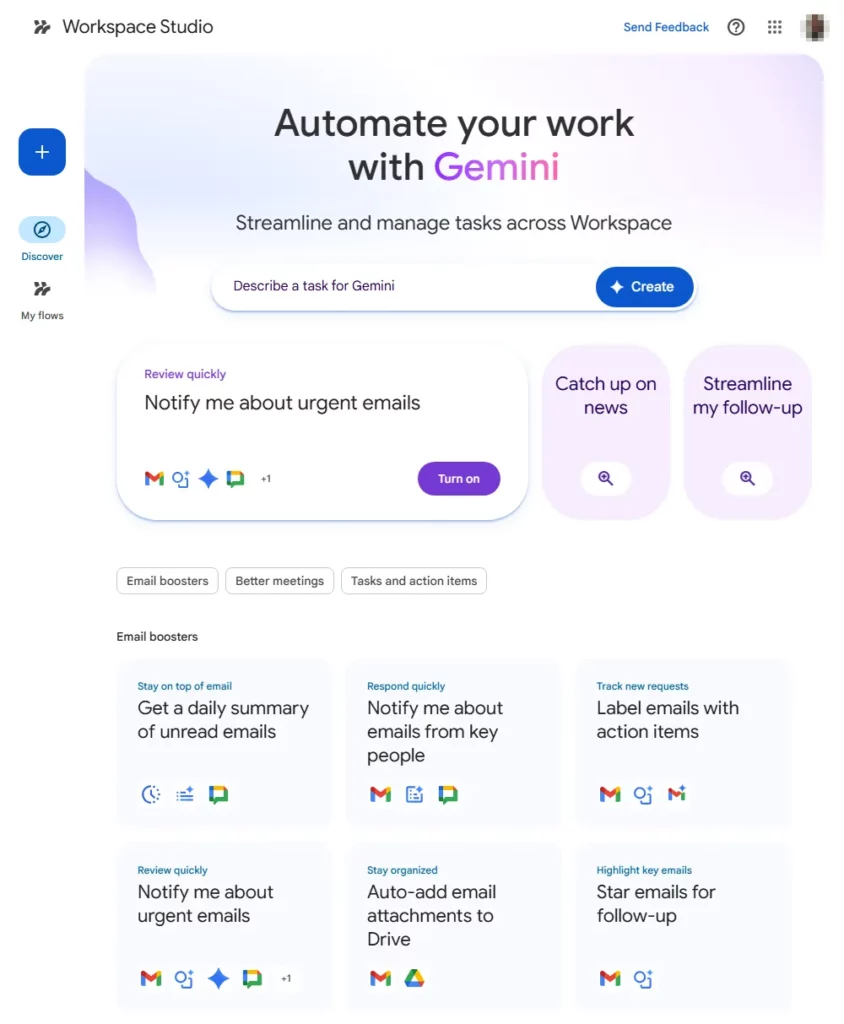
The Flow Builder is where you construct agents. It’s a vertical, linear timeline where you click the + button to insert steps. The right-hand sidebar provides configuration options for each step, including variable mapping and prompt engineering fields.
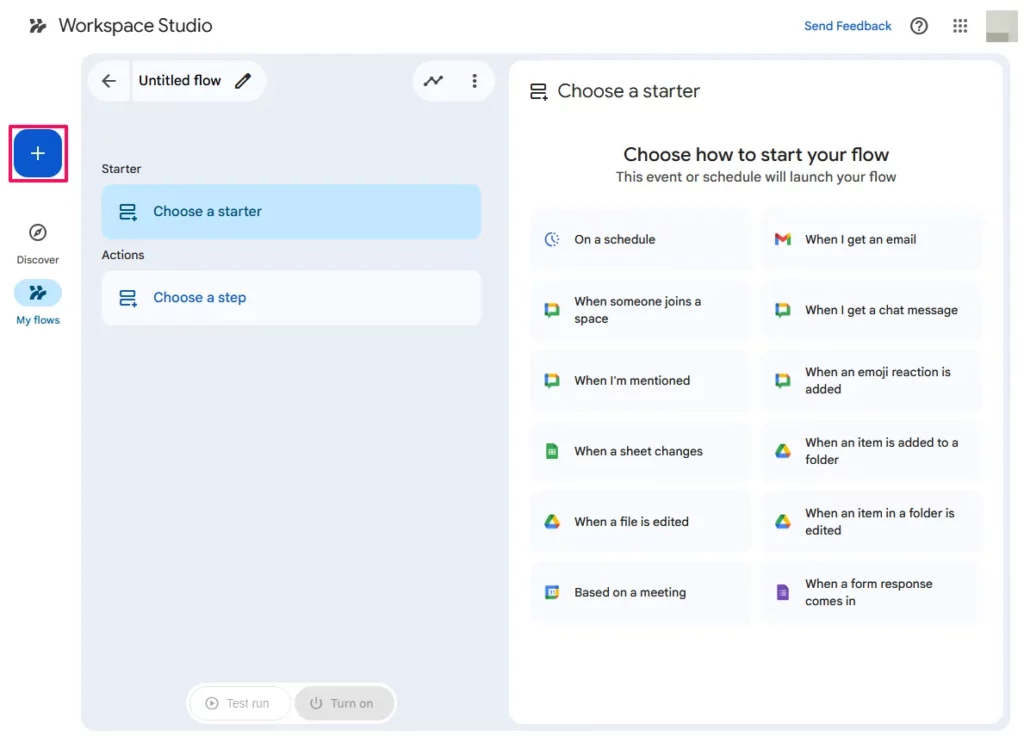
My Flows is your dashboard for managing existing agents. It provides a list view with toggle switches to instantly enable or pause flows, plus a “Last Run” status for health monitoring.
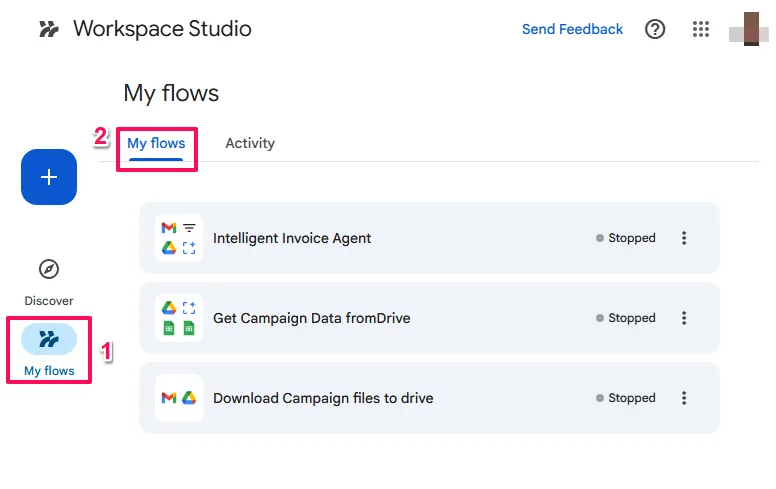
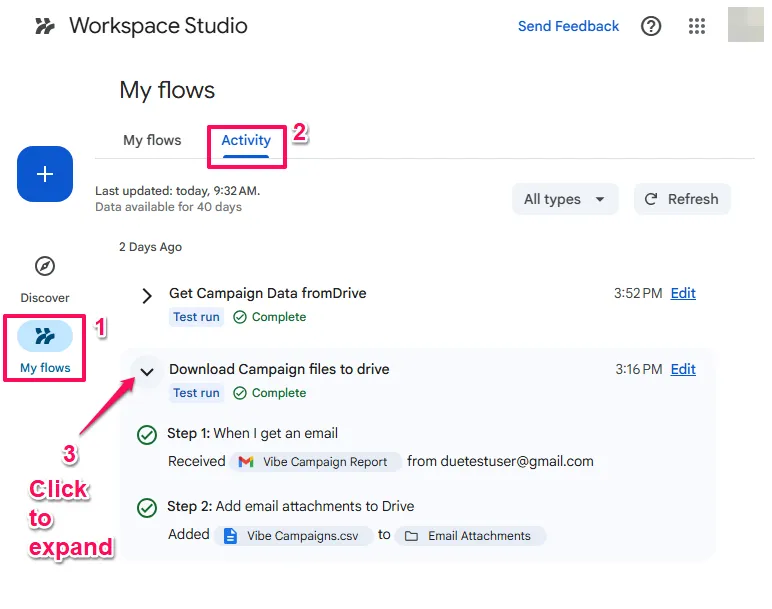
Activity & Logs is critical for debugging. You can drill down into specific runs to see exactly what data entered and exited each step. This is essential for diagnosing why a Decide step returned False when you expected True.
Your First Flow: A Personal Briefing Agent
The best way to understand the system is to build something simple but useful. Let’s create an agent that sends you a morning summary of important emails.
Scenario: You start your day with an overloaded inbox. Instead of manually checking your inbox first thing, this agent automatically triages your inbox while you sleep. At 8:00 AM, it identifies unread emails from a specific timeframe, categorises them by urgency and theme, and sends a beautifully formatted summary to your Google Chat.

Creating the Flow:
- Access the Workspace Studio
- Go to
studio.workspace.google.com
- Go to
- Start from Scratch
- On the Discover page, click
+New Flow(or use theDescribe a task for Geminibar and type “Send me a daily summary of VIP emails in Chat”)
- On the Discover page, click
- Name Your Agent
- Click the pencil icon at the top left to rename your flow from “Untitled” to “Morning Briefing Bot”
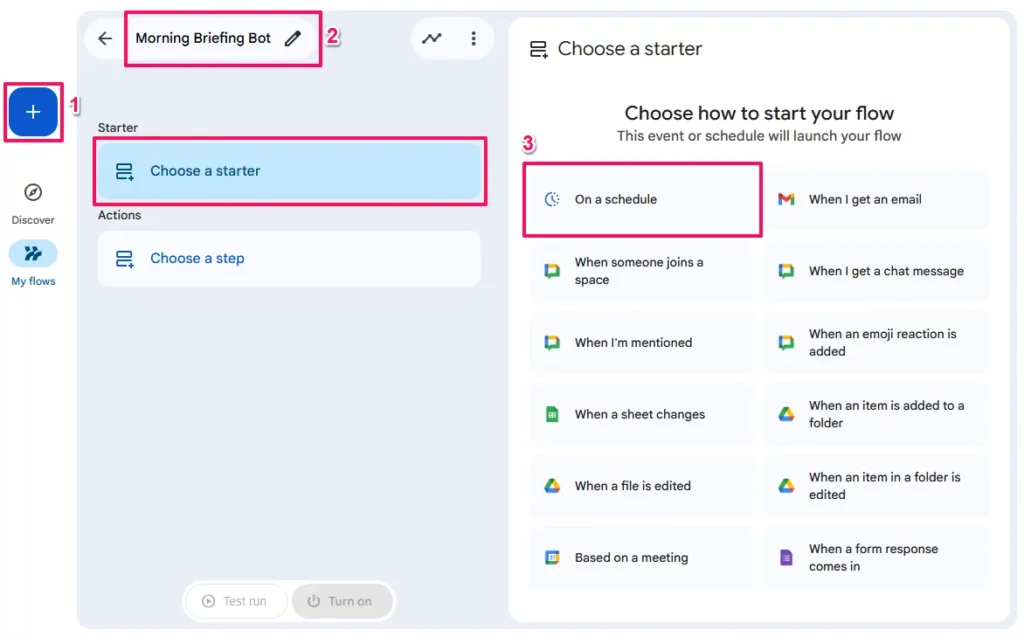
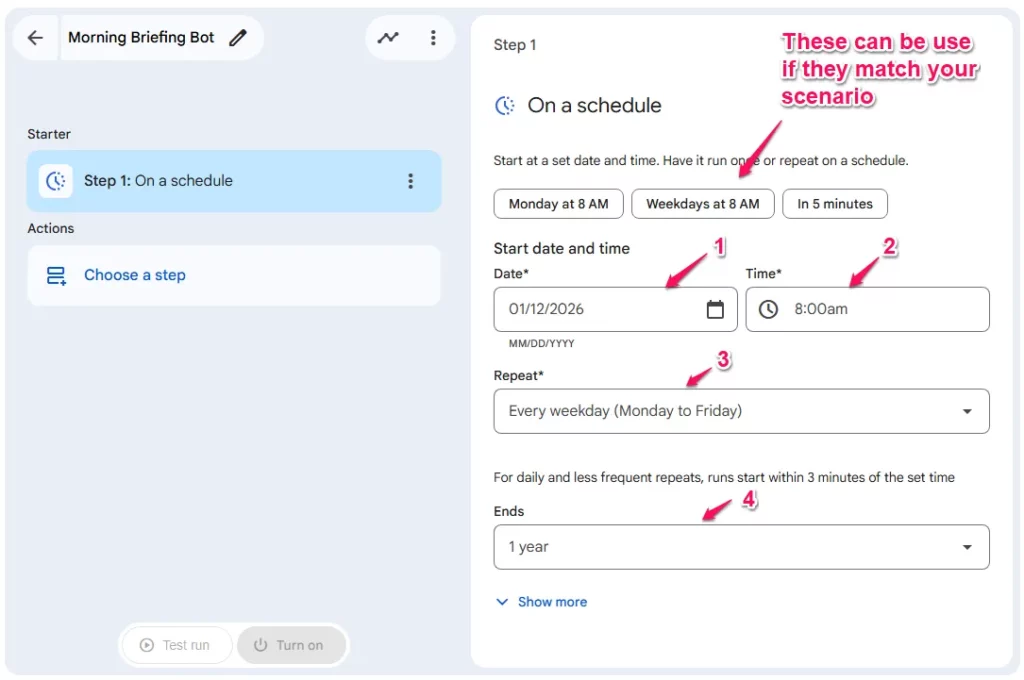
Step 1: The Starter (The Trigger)
- Click
Choose a starterand selectOn a schedule. - Configuration:
- In the
Start date and time sectionselect aDateand set theTimetime to8:00am. - For
Repeat, selectEvery weekday (Monday to Friday)from the dropdown. - You can also select when it
Ends.
- In the
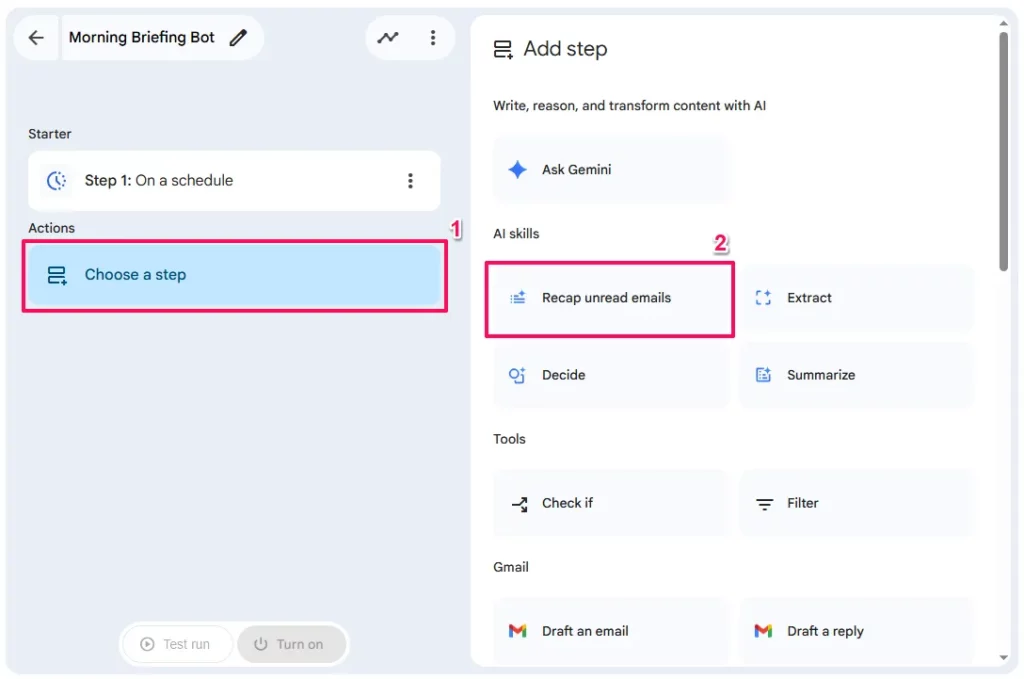
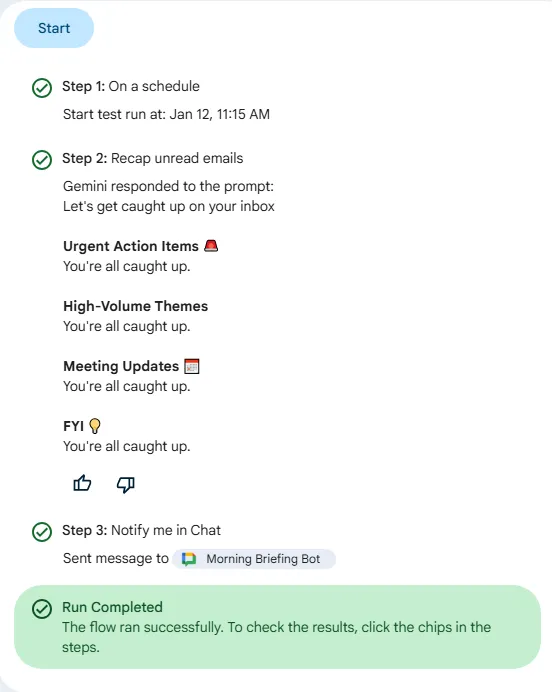
Step 2: The Intelligence (Recap unread emails)
- Click the
Choose a stepbelow your starter and selectRecap unread emailsstep from theAI skillssection.
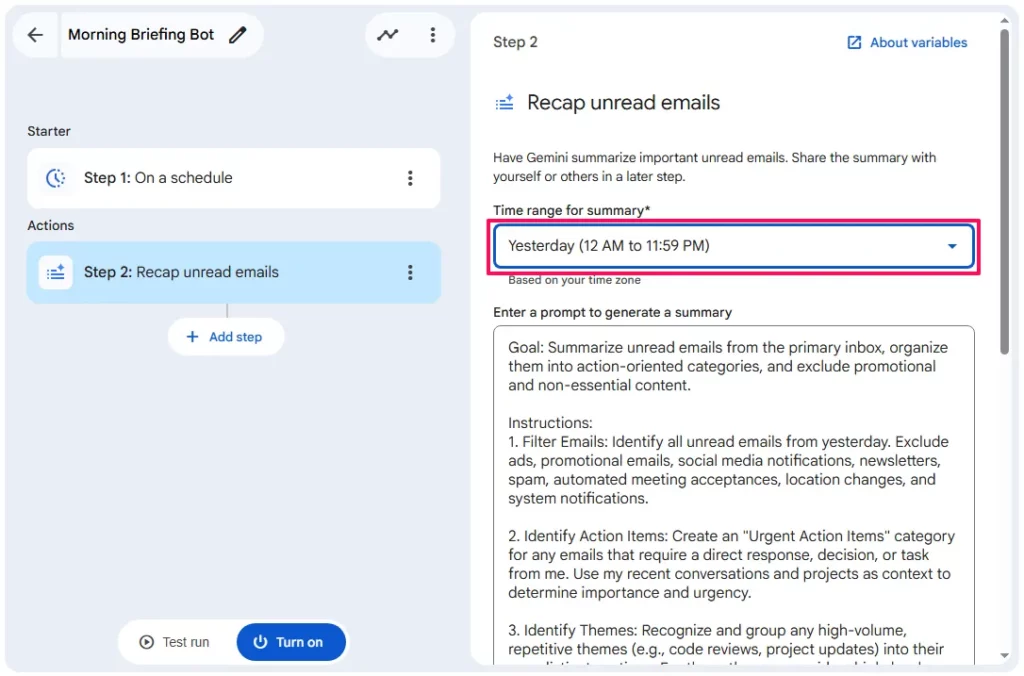
- Configuration:
Time range for summary- Select
Yesterday (12 AM to 11:59 PM)from the dropdown
- Select
Enter a prompt to generate a summary- This field comes with a sophisticated default prompt. This prompt is designed to:
- Filter content: It automatically excludes ads, social media notifications, newsletters, and spam
- Identify Action Items: It creates an “Urgent Action Items” category for emails requiring a direct response
- Theme Grouping: It groups repetitive themes, such as project updates, into high-level summaries rather than listing every individual email
- Customisation Tip:
- You can edit this prompt to be more specific, such as adding “Focus specifically on emails from [Client Name]” to further refine the results
- This field comes with a sophisticated default prompt. This prompt is designed to:
Step 3: The Delivery (Google Chat)
- Click
+ Add step.
- Select
Notify me in Chat.
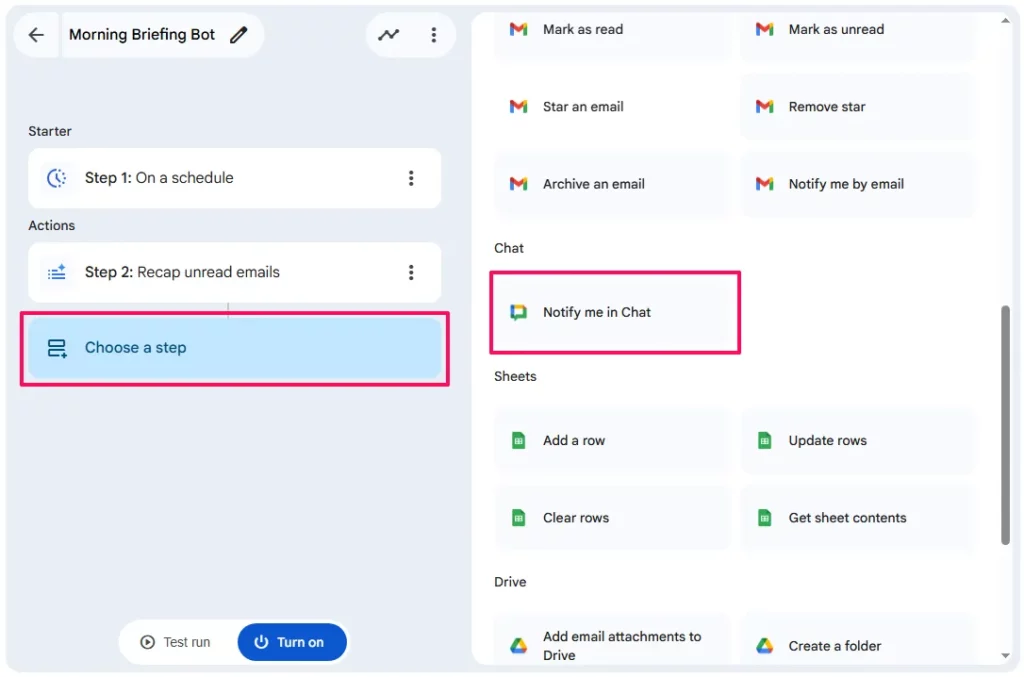
- Message Body:
- Click into the
Messagefield and type the @ symbol (or click+ Variables)
- Click into the
- Select the Variable:
- From the list, choose
Step 2: Summary of unread email. It will appear as a coloured chip in your text
- From the list, choose

or

This passes the AI’s categorised summary into your chat message.
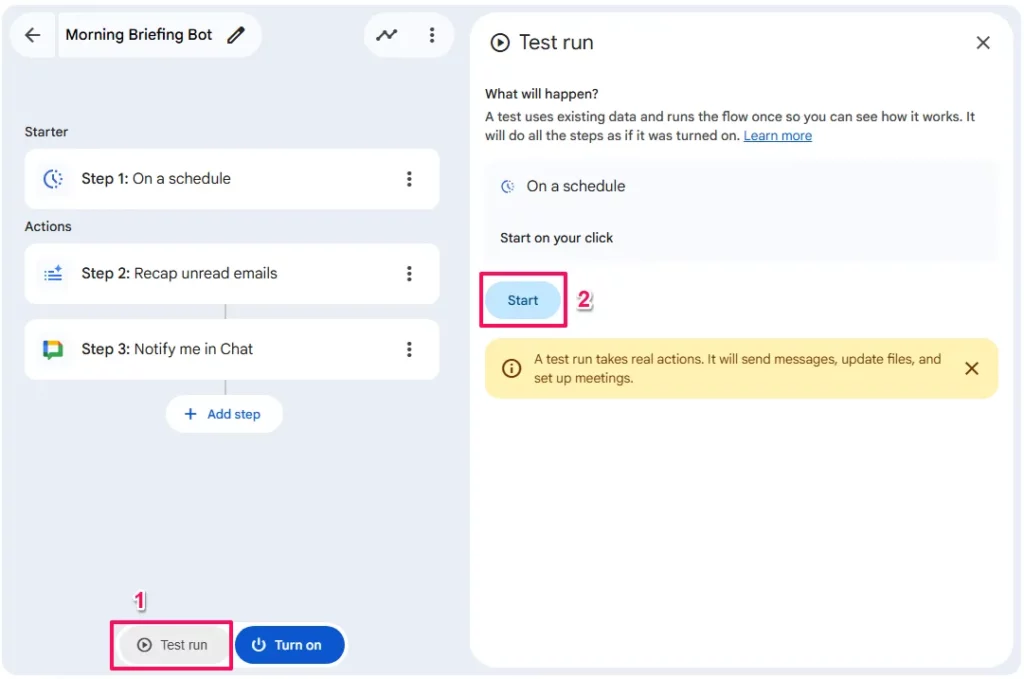
Activation and Testing
- Test Run:
- If you don’t want to wait until 8:00 AM, click
Test runto execute the flow immediately and see the results in the Activity tab
- If you don’t want to wait until 8:00 AM, click
- Find Your Results:
- Your briefing will not appear as a standard DM from a person. Instead, look in the “Apps” section at the bottom of your Google Chat sidebar. You will see a new app named “Morning Briefing Bot” (the name of your flow)
- Turn On: Click the Turn on toggle
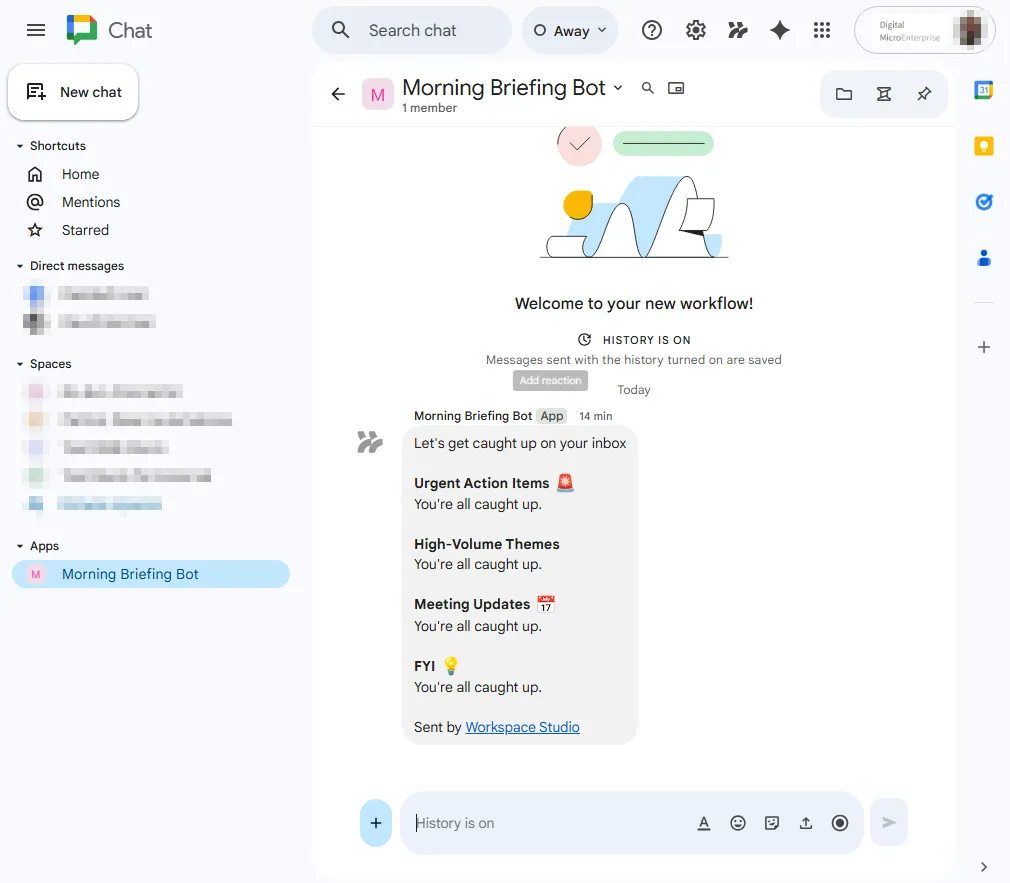
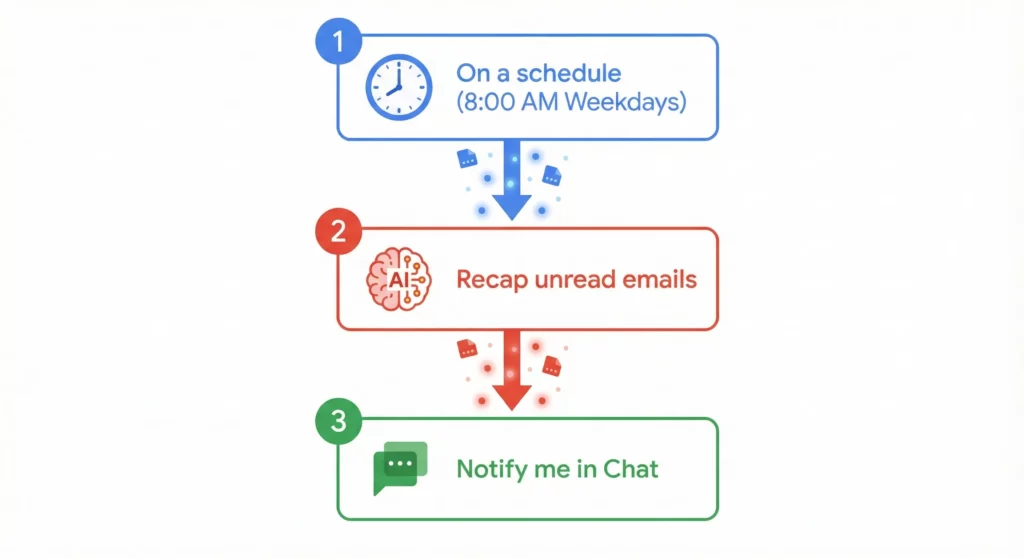
This simple three-step flow demonstrates the core loop: Trigger (Time) → Intelligence (Summarisation) → Action (Communication).
Key Capabilities That Set Workspace Studio Apart
Advanced Event Monitoring
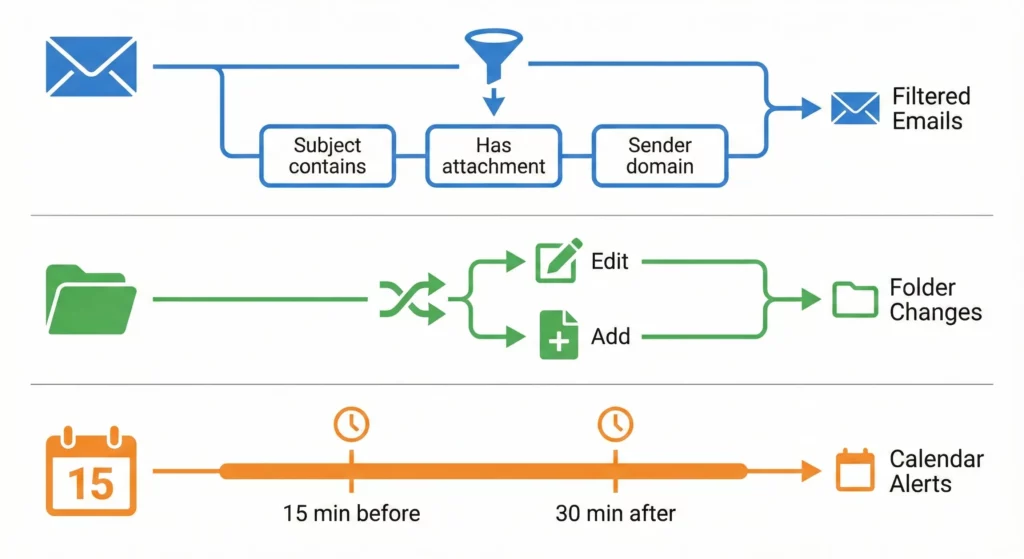
The Starter mechanism is more sophisticated than simple triggers. It includes pre-flight filtering that’s essential for quota management.
Granular Email Filtering doesn’t just fire on “New Email.” You can configure Boolean logic at the trigger level: Subject CONTAINS "Invoice" AND HasAttachment == TRUE AND SenderDomain != "internal.com". Setting this up correctly is the single most important step in preventing runaway automation that exhausts your daily limits.
File Event Nuance distinguishes between files being added versus edited. The File Edited starter detects content changes but currently doesn’t trigger on metadata changes like moving (though this feature in Google Drive is currently in developer preview). However, simply renaming a file still generally does not trigger a Content Edited flow.
Calendar Context with the Based on a meeting starter allows for relative time triggers (15 minutes before, 30 minutes after). It carries event metadata into your flow, enabling highly contextual preparation or follow-up actions.
The AI Reasoning Engine

Gemini integration enables steps that were previously impossible in automation.
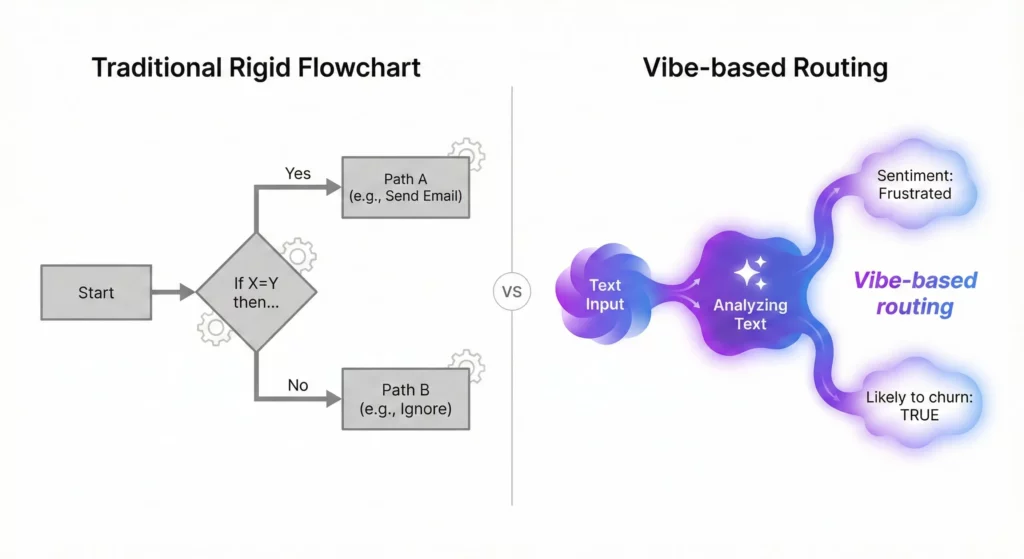
The Decide Step is a probabilistic logic gate. Unlike standard conditional checks that compare strings, Decide evaluates sentiment and intent. You can ask it: “Is this email from a frustrated customer who is likely to churn?” The system feeds the email body and your prompt to Gemini, which returns a Boolean to guide your flow. This enables what you might call “vibe-based” routing.
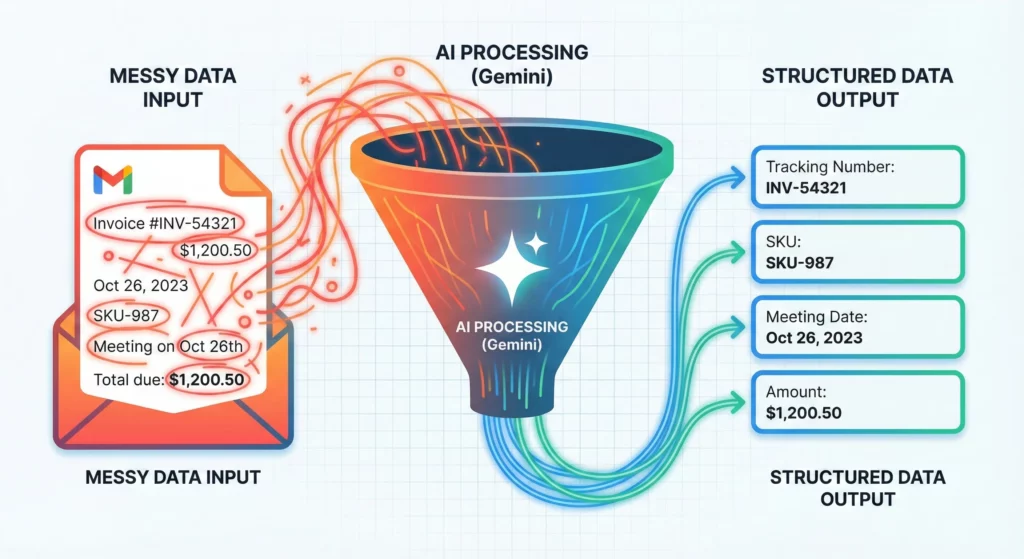
The Extract Step uses Gemini’s Named Entity Recognition capabilities. It can ingest a PDF, image, or messy email thread and extract specific entities you define (Tracking Number, SKU, Meeting Date). It creates structured variables from these entities, essentially cleaning messy human data for machine processing.
Prompt Engineering in Ask Gemini gives you a blank canvas. You can use sophisticated prompting techniques (Few-Shot Prompting, Chain-of-Thought) to guide the AI’s output. For example, you might provide three examples of your desired writing style to ensure drafted emails match your voice.
Native Application Integration
Workspace Studio has superuser access to Google Apps, often bypassing the limitations of public APIs.
Gmail flows can manage labels, mark messages as read or unread, and draft replies in your Drafts folder (a best practice for human review before sending).
Drive flows can manage folder hierarchies, move files, and control permissions. The file iterator capability (processing all files in a folder) is particularly useful for batch organisation.
Chat flows can interact with specific Spaces and distinguish between threaded replies and new conversations, enabling organised automated discourse.
Sheets flows can use Update Row and Find Row steps to function as a lightweight relational database. You can look up a customer ID in Column A and update Status in Column F, effectively turning Sheets into a CRM backend.
Connectivity and Extensibility (Currently in Limited Preview)
Limited Preview. There is currently no way to request access to the limited preview
Workspace Studio connects to the external world through two primary mechanisms.
Webhooks: Your Digital Messenger
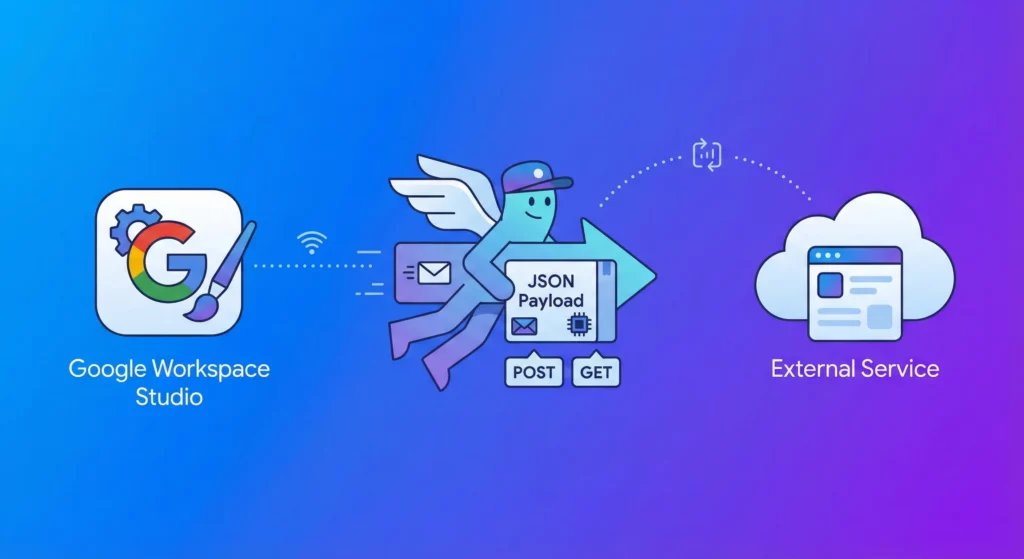
Think of a webhook as a way for your flow to send a specific message to another app. A webhook step sends an HTTP request to a URL you provide, allowing you to trigger actions in external services.
• How it works: You provide a static URL for the external service and choose a “method” (like POST to create something new or GET to retrieve data).
• The Payload: This is the actual information you are sending, such as a customer’s name or an email summary. We recommend using JSON format for this, as it is the standard language web services use to talk to each other.
• Example: You could set up a flow that, upon receiving an “Urgent” email, automatically sends a webhook to Slack to post a message in an emergency channel
Third-Party Integrations: Ready-to-Use Connections
For those who don’t want to deal with URLs and payloads, Workspace Studio offers pre-built integrations. These allow you to drag and drop actions from popular business apps directly into your execution chain.
• Common Connectors: You can currently find integrations for Asana, Jira, Mailchimp, and Salesforce.
• Simple Setup: These integrations handle the technical “handshaking” (OAuth authentication) for you. You simply connect your account through the Google Workspace Marketplace and follow the on-screen instructions.
• Beginner Tip: Always make sure you trust the third-party service before connecting it, as your flows may share sensitive Google Account data, like Gmail message contents or Calendar event details, with that service
Add-on Extensions: Custom Power with Apps Script

If a pre-built step doesn’t exist for your specific needs, you (or a developer in your organisation) can build one using Google Apps Script.
• Custom Steps: These are tasks tailored to your specific business logic that can be shared across your organisation.
• Complex Data Handling: For more advanced users, extensions allow for Dynamic Variables (information that changes based on what you select during setup, like specific questions in a Google Form) and Custom Resources (which group multiple related variables together, like a customer’s name, email, and address)
Advanced AI: Ask a Gem
Extensibility also includes specialised AI agents called Gems. In the Ask a Gem step, you can use an AI agent that has been pre-trained for a very specific expertise, such as a “Brainstormer” or a “Sales Pitch Ideator,” rather than just asking general questions to Gemini
Building Your First Agents: Detailed Tutorials
Tutorial 1: The Meeting Sentinel
Scenario: You spend hours every week digging through emails to find context for upcoming meetings.
Objective: An agent that wakes up 15 minutes before every meeting, scans your email for correspondence with attendees, summarises the context, and sends you a briefing in Chat.
Construction:
- Starter: Select
Based on a meeting- Configuration: Starts 15 minutes before the event.
- Filter:
Event Status is ConfirmedANDOrganizer is NOT Me(avoiding meetings you created and already know about) - Note: This starter automatically provides variables for the
Event Title,Description (Agenda),Attendees, andAttachments.
- Step 1: Intelligent Summarisation
- Action: Summarise (AI Skill Step)
- Query:
from:[Attendee Emails] - Limit: Last 5 emails
- Step 2: Synthesise Briefing
- Action:
Ask Gemini - Prompt: “I have a meeting titled ‘[Event Title]’. Based on this summary of the agenda and materials: [Step 1 Summary Variable], provide a list of key discussion points and any actionable items I should be aware of. Keep it bulleted and under 200 words.”
- Action:
- Step 3: Deliver Briefing
- Action:
Notify me in Chat - Recipient: Me (Direct Message)
- Message Body: “📅 Pre-Meeting Brief: \n\n[Event Title]\n\n[Gemini Response Variable]\n\nGenerated by Workspace Studio.”
- Action:
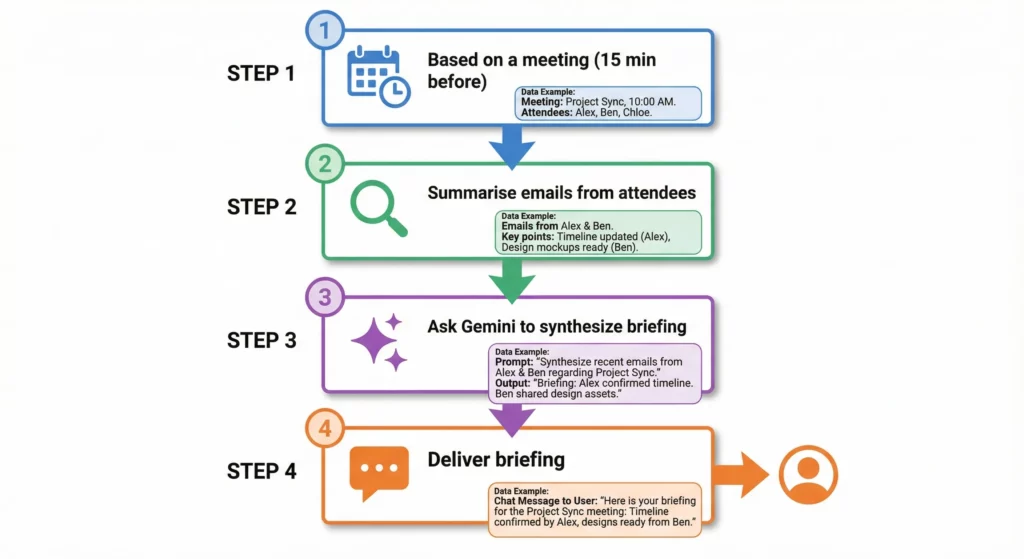
Outcome: You enter every meeting prepared, without manual searching.
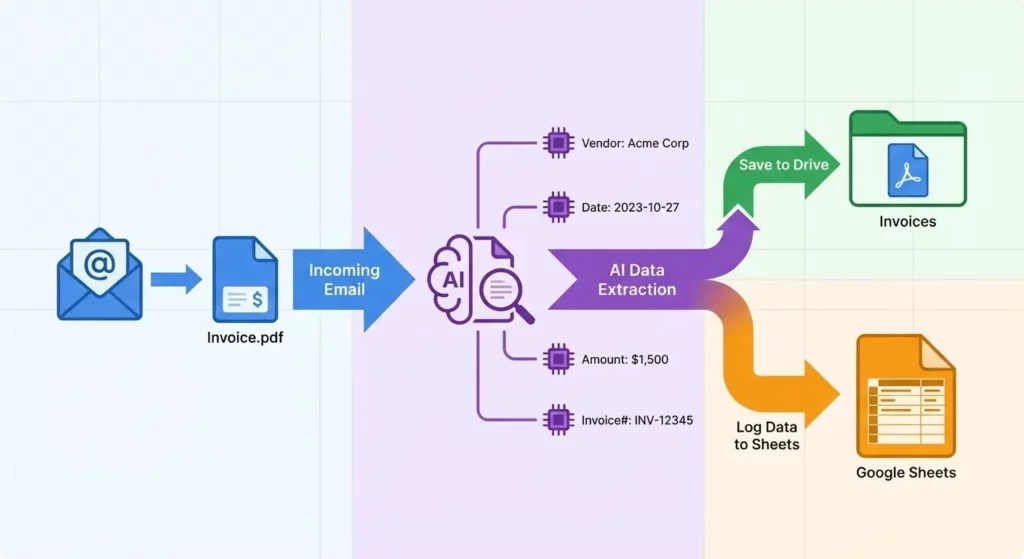
Tutorial 2: The Invoice Bot
Scenario: Vendors send PDF invoices to your email. You manually save them to Drive and log amounts in a Sheet.
Objective: Automate the extraction and logging of invoice data.
Construction:
- Starter:
When I get an email- Filter: (
Subject CONTAINS "Invoice"ORSubject CONTAINS "Bill") ANDHasAttachment == TRUE
- Filter: (
- Step 1: Isolate the File
- Action:
Filter a list - Input: [Message Attachments]
- Condition:
MimeType CONTAINS "pdf"
- Action:
- Step 2: Intelligent Extraction
- Action:
Extract - Input: [Filtered Attachments]
- Fields to Extract: Vendor Name (Text), Invoice Date (Date), Total Amount (Number), Invoice Number (Text)
- Action:
- Step 3: Save to Drive
- Action:
Move file - Input: [Filtered Attachments]
- Destination:
Finance/Invoices/2026
- Action:
- Step 4: Log to Sheets
- Action:
Add a row - Sheet: Expense Log 2026
- Mapping: Map the variables from the Extract step to columns (A: Vendor, B: Date, C: Amount, D: File Link)
- Action:
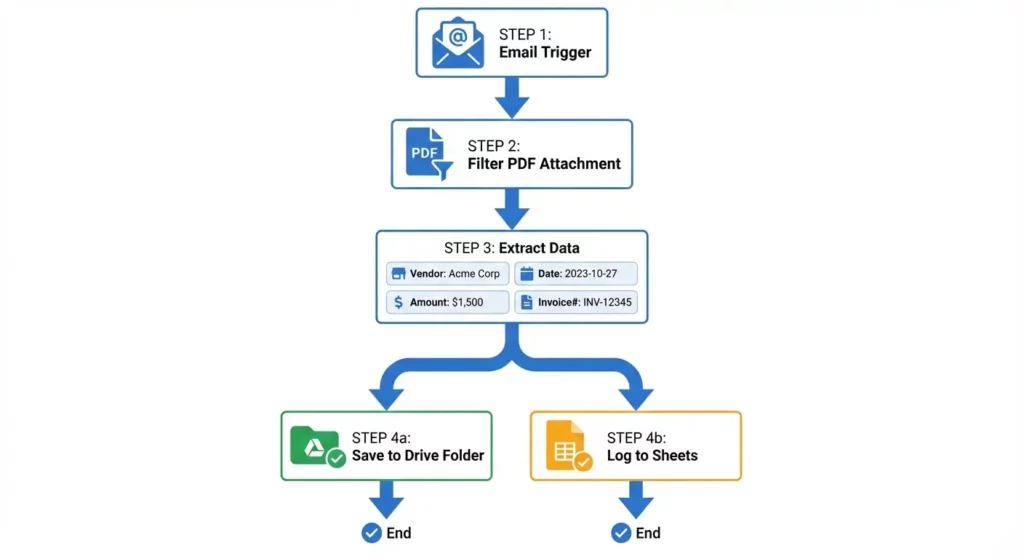
Outcome: A fully automated Accounts Payable ingestion engine.
Tutorial 3: The Sales Lead Router
This uses features that are only available as part of Limited Preview
Scenario: A “Contact Us” form on your website collects leads. You want to route high-value leads to Salesforce and low-value leads to an email nurture sequence.
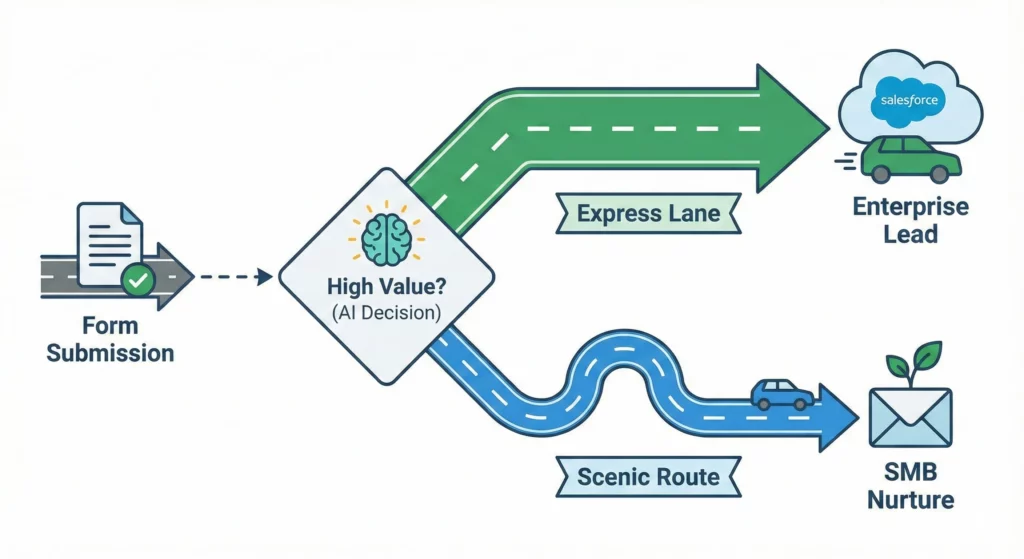
Construction:
- Starter:
When a form response comes in- Source: Contact Us Form
- Step 1: Qualify
- Action:
Decide - Prompt: “Analyse this lead inquiry: [Form Response]. Is this a high-value enterprise lead (asking for bulk pricing, 100+ seats, or from a Fortune 500 domain)? Return TRUE for Enterprise, FALSE for SMB.”
- Action:
- Step 2: Branching Logic
- Action:
Check if - Condition: [Decide Result] IS
True
- Action:
- Step 3A (True Branch): Send to Salesforce
- Action:
Create Record(Salesforce Connector) - Object: Lead
- Fields: Map Name, Email, and Company from Form Response. Set Status to “New – Hot”
- Action:
- Step 3B (False Branch): Webhook to Marketing Tool
- Action:
Send a webhook - URL:
https://api.mailchimp.com/3.0/lists/... - Method:
POST - Payload:
{ "email": "[Email Variable]", "tags": ["nurture_sequence"] }
- Action:
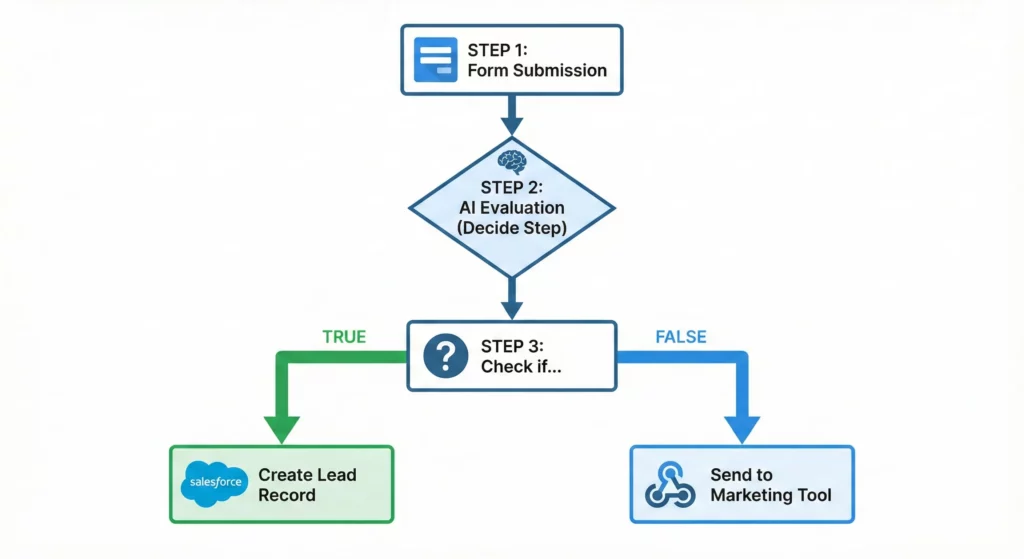
Outcome: Automated lead qualification that prioritises high-value prospects instantly.
How Workspace Studio Compares to Other Automation Tools
To understand where Workspace Studio fits, you need to see it in the context of the broader automation market dominated by Zapier, Make, n8n, and Zenphi.
The Cost and Security Advantage
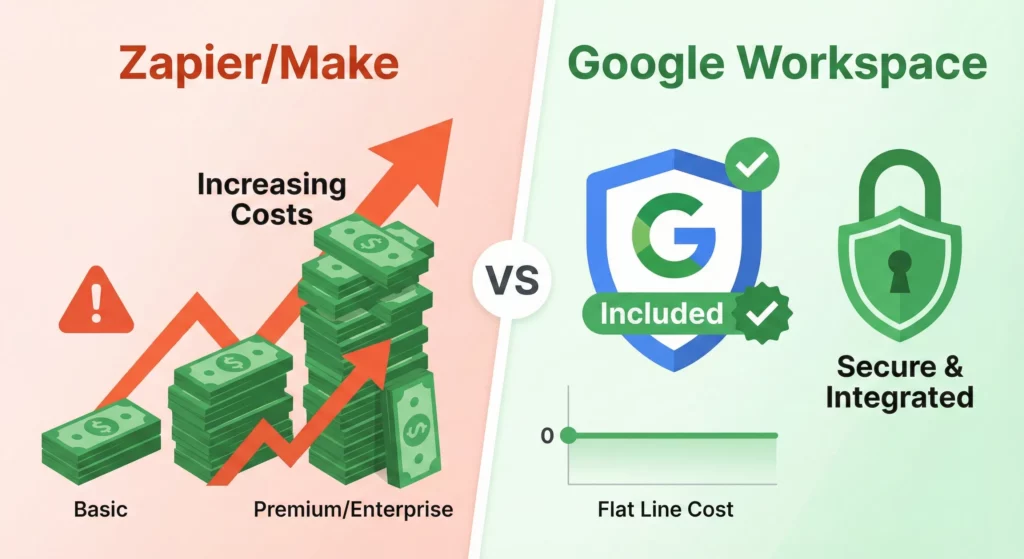
For existing Google Workspace Business and Enterprise customers, Workspace Studio is largely included in your subscription. Compare this to Zapier or Make, which charge by the task or operation. A company running 10,000 automations monthly could pay hundreds to Zapier – with Workspace Studio, this cost is absorbed into your seat licence (subject to daily limits).
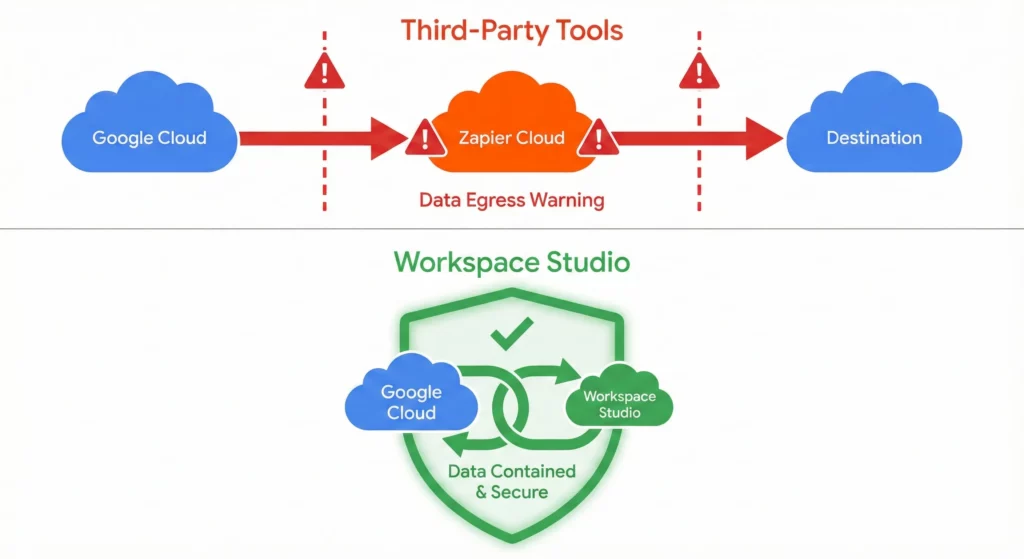
Third-party tools like Zapier require your data to leave the Google tenant. An email arrives in Gmail, gets sent to Zapier’s servers for processing, then action is taken. This data egress creates security vulnerabilities and compliance headaches (GDPR, HIPAA). Workspace Studio processes data within the Google compliance boundary; a massive advantage for regulated industries.
Competitor Comparison
Here’s how Workspace Studio compares to the main alternatives:
| Feature | Google Workspace Studio | n8n | Zenphi | Zapier |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary User | Business Analyst / Generalist | Developer / Technical Ops | Enterprise Process Architect | SMB / Generalist |
| Architecture | SaaS (Google Cloud) | Self-Hosted or Cloud | SaaS (Google Cloud) | SaaS |
| Logic Model | Agentic (AI/Probabilistic) | Deterministic (Node-based) | Process-Oriented (BPMN) | Deterministic (Trigger-Action) |
| Data Sovereignty | High (Stays in Google) | Highest (Self-Hosted) | High (Google Native) | Low (Third-Party Processing) |
| Complexity Limit | Low (20 Steps, No Loops) | High (Infinite Complexity) | High (State Machines) | Medium (Multi-step Zaps) |
| Pricing | Included in Workspace* | Licensing / Free Community | Subscription | Usage-Based (Task count) |
n8n remains superior for complex, technical orchestration. If you need to transform massive JSON arrays, run Python scripts, or connect to on-premise SQL databases via VPN, n8n is the tool. Workspace Studio can’t match n8n’s flexibility or self-hosting capability.
Zenphi positions itself as a “Business Process Automation” tool rather than a “Task Automation” tool. It handles long-running state (like a document approval process taking three weeks and involving five people). Workspace Studio flows are transient, they run and finish. Zenphi also offers deeper admin governance features that Workspace Studio currently lacks.
Zapier remains the king of connectivity. With 6,000+ apps, if you need to connect to a niche marketing tool or specific project management software not supported by Google’s limited Marketplace, Zapier is still necessary.
Understanding the Limitations
Google is providing promotional access to higher usage limits of Workspace Studio to allow users to experiment with these features. However, usage may be subject to change to ensure consistent performance for all users.
The following are the limits as of January 2026:
Capacity and Quotas
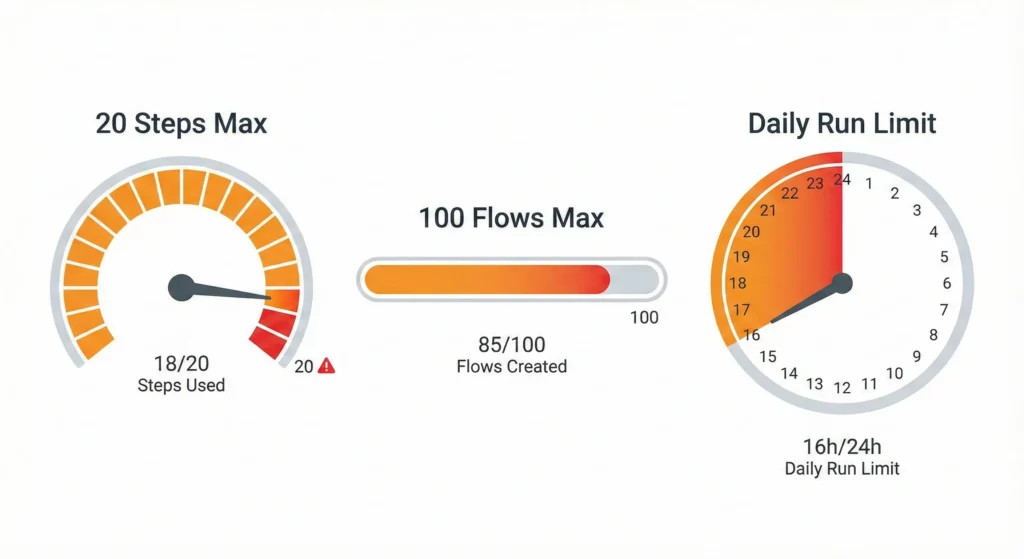
- The 20-Step Ceiling means a single flow cannot exceed 20 steps. This forces you to break complex processes into smaller, daisy-chained flows, which can make debugging difficult.
- Flow Creation Cap: You can create a maximum of 100 total flows per account, which includes both active and inactive (turned off) agents.
- Gmail Starter Restrictions: To manage high-frequency events, a maximum of 25 active flows can be triggered by Gmail starters at any one time.
- Daily Run Limit: There is a combined maximum number of times all of your flows can run within a 24-hour period. If this limit is reached, all active flows will stop running until the limit resets.
- Gemini Prompt Limits: When using AI steps like “Ask Gemini” or “Decide”, your total prompt must remain under approximately 144,000 characters (roughly 18,000 words). This limit is cumulative, meaning it includes your manual instructions, all content added via variables (such as a “Message Body”), and any linked content. If a flow attempts to process a very long email thread or a massive document that pushes the prompt over this ceiling, the run will fail with an error. To avoid this, consider using fewer variables or ensuring the source data is concise.
Performance
- Latency is real for AI steps. A
Decidestep involves an LLM inference call, which can take 2-5 seconds. Workspace Studio isn’t suitable for real-time, sub-second latency requirements.
Logic and Conditional Constraints
Workspace Studio’s linear design results in specific limitations for branching logic:
- Variable Isolation: You cannot use variables generated within a conditional substep (like an “Ask Gemini” result inside a “Check if” branch) in later steps of the main flow.
- No Nesting: Flows cannot have nested conditional steps. You cannot place a “Check if” or “Decide” step inside the substeps of another conditional block.
- Operator Uniformity: When setting multiple conditions in a “Check if” step, you must choose either AND or OR; you cannot mix these operators within a single step.
- No Native Loops means you can’t iterate over a list of items within a flow. If a sheet change provides 10 modified rows, the flow processes them as a batch or processes only the first one, depending on configuration. You can’t say “For Each Row, Send Email”; a significant limitation compared to Apps Script or n8n.
Identity and Context Limitations
- The User Context Problem means flows execute with the permissions of the flow owner. If the owner loses access to a shared folder, the flow fails. There’s currently no concept of a “System Flow” that runs with elevated, independent privileges. This links automation fragility to employee turnover.
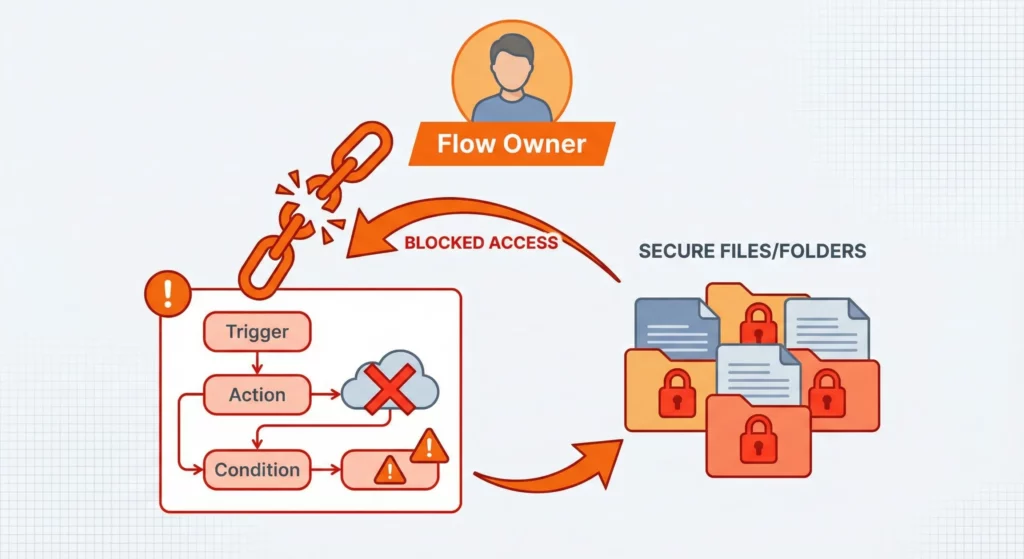
- Approval Workflow Gaps are significant. The platform lacks a built-in “Wait for Approval” state. You can’t pause a flow for two days while a manager reviews a document. You must construct workarounds using two separate flows (Request Flow and Approval Response Flow), which is cumbersome compared to Zenphi’s native approval steps.
Security and Access Limitations
- Age Restrictions: Users under 18 on school accounts are strictly prohibited from using any AI features; AI steps will be automatically removed if a flow is shared with them.
- Device Requirements: You must use a computer with a supported web browser to create or edit flows. Workspace Studio is not available for flow creation on mobile devices.
- File Permissions: Flows may fail to update files if the file is shared with other people or groups; it is recommended to use files that only you can access for automated updates.
Users under 18 (in K-12 Education domains) are blocked from using AI features in Workspace Studio, significantly limiting education sector use cases.
Best Practices for Production Deployment
Governance and Security

Administrators must actively manage the environment. This means:
- Setting clear policies on what types of automation are permitted
- Regularly auditing active flows to prevent data sprawl
- Establishing naming conventions for flows to make them discoverable
- Creating documentation standards so flows can be maintained when employees leave
Education and Training
Users need training not just on how to build flows, but when to use AI versus standard logic. Some decisions benefit from AI’s flexibility, while others require the predictability of deterministic rules.
Create internal champions who can help colleagues design flows effectively. The democratisation of automation doesn’t mean everyone should automate everything; it means the right people should automate the right things.
Strategic Positioning
Define where Workspace Studio fits in your broader automation stack. For simple, Google-native workflows with AI requirements, Studio is ideal. For complex, multi-system orchestration or long-running approval processes, you may need Zenphi or n8n alongside Studio.
Don’t force Workspace Studio into use cases where its limitations create more problems than it solves. The 20-step limit and lack of loops make certain workflows genuinely difficult.
Next Steps
If you’re ready to implement Google Workspace Studio, start with these immediate actions:
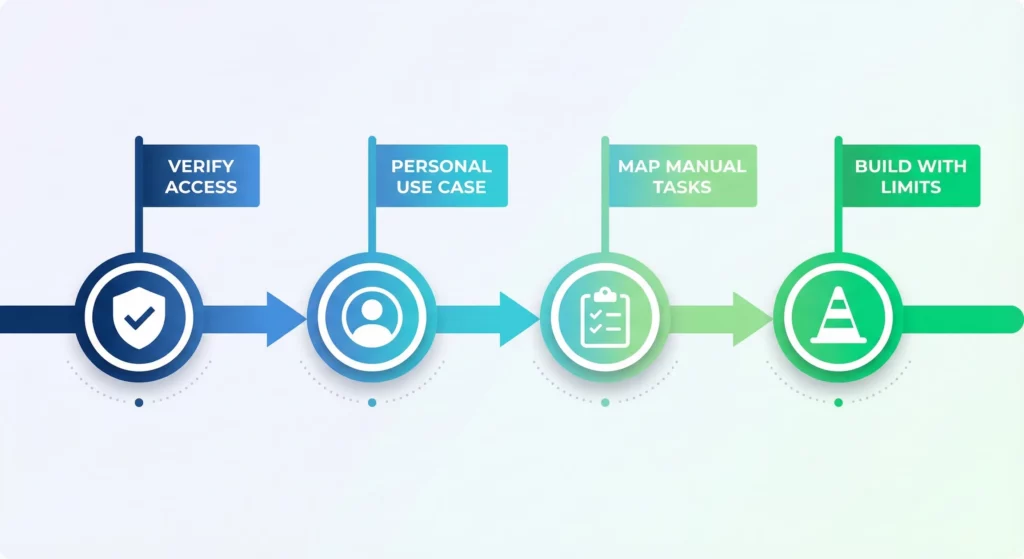
Verify your organisation has Workspace Studio enabled. Check with your Google Workspace Administrator whether the service is turned on for your Organisational Unit. If not, request activation.
Start with a personal use case. Don’t begin by automating critical business processes. Build a simple flow that solves your own problem; like the morning briefing agent or automated file organisation. This builds your understanding without risking business operations.
Map your most time-consuming manual tasks. Spend a day noting every time you manually move data between systems or perform repetitive categorisation. These are your highest-value automation targets.
Build with the limitations in mind. Design flows that stay within the 20-step limit. If you need more complexity, plan how you’ll chain multiple flows together. Accept that some workflows genuinely aren’t suitable for Workspace Studio yet.
Google Workspace Studio represents a significant capability, but it’s a tool that requires thoughtful implementation. Success comes from understanding both its strengths and its constraints, then applying it strategically where it genuinely improves productivity.
Conclusion
The release of Google Workspace Studio marks the moment when AI agents transitioned from theoretical concept to practical utility in everyday work. For organisations, it presents a genuine opportunity to reclaim lost productivity, the hours spent moving data from email to sheets, from Drive to Chat, can now be handled by Gemini.
But Workspace Studio isn’t a magic solution. It’s a tool that requires governance, education, and strategy. Administrators must manage the environment to prevent security risks. Users must understand when to use AI versus standard logic. Organisations must define where Studio fits alongside other automation tools in their stack.
As we move deeper into 2026, Google will likely address current limitations like loops and service accounts. But the capabilities available today are already sufficient to transform personal and team productivity. The question isn’t whether to use Workspace Studio; it’s how to use it strategically, with clear understanding of both its power and its constraints.
